In the previous part of this guide regarding the use of thermal imaging in practice, we focused at a general explanation of how it works, the main differences in its application compared to night vision, and we looked at some popular theories related to the properties of thermal imaging.
Browsing through the offers of stores, you can come across a huge variety of products and extensive technical specifications of devices. What should youpay attention to when choosing your own thermal imager? How do individual parameters and features of devices affect the experience of using them? In this article, we try to describe the differences between the designs and bring you closer to the meaning of selected parameters which, in our opinion, are important when making decisions.
2022 Delta Optical Neon S1 thermal sight. The photo also shows camouflages made in Poland - by Sniper Ghillie Systems.
For the comfort of the readers, we have decided to divide this part of the guide into two chapters. The first one includes:
- Imager types
- Sensor resolution
- Base zoom, field of view, lens size
- Device range
- Refresh rate
- Pixels size - 17 um or 12 um?
In chapter two, which will be released next week, we will look at the issues of thermal sensitivity (NETD), methods of NUC correction, types of power supply, algorithms responsible for image quality, resistance standards and other noteworthy aspects.
Imager types
There are many types of thermal imagers - e.g. monocular, clip-on, binoculars, scopes. How does one decide on the right one? It all depends on the intended use for the device.
2023 Some thermal imaging monoculars (as the ATN Odin LT 640 in the photo) are designed to be worn on one's head.
If the device is to be used mainly for observation or movement, handheld thermal imagers, including those compatible with various types of head mounts, may be a sensible choice. If you want to use thermal imaging during activities involving shooting, it may be necessary to buy a proper sight or a thermal imaging attachment mounted on daytime optics. The latter is quite a versatile solution, which sometimes offers the possibility of transforming the device into an observation monocular. Such universality may be valuable for some, but in principle it will work worse in relation to dedicated solutions of a specific type.
2018. Discontinued Leupold LTO Tracker Series Handheld Imagers are distinguished by the use of an external display instead of the classic viewfinder. Observation is carried out by looking a screen similarly to a phone. Third-party viewfinder adapters are also available on the market.
The thermal imagers available on the market are diverse in terms of their construction and technical parameters. Their individual types, due to their purpose, may require completely different specifications (e.g. low magnification for devices worn on the head). It is also not uncommon for an individual to invest in more than one type of device to experience the full benefits of thermal imaging.
Sensor resolution
The resolution of the sensor should not be confused with the resolution of the screen on which the thermal image is displayed. The former, is one of the basic parameters that quickly catches the eye when searching through the offers of stores (sometimes it is even included in the product name itself). Manufacturers often emphasize the visibility of information about the resolution of the thermal sensor, as this is one of the factors having the greatest influence on image quality and the final price of a thermal imager intended for the civilian market. Due to various technical issues related to thermal imaging, it is hard to find models with resolutions similar to those of today's digital cameras and camcorders.
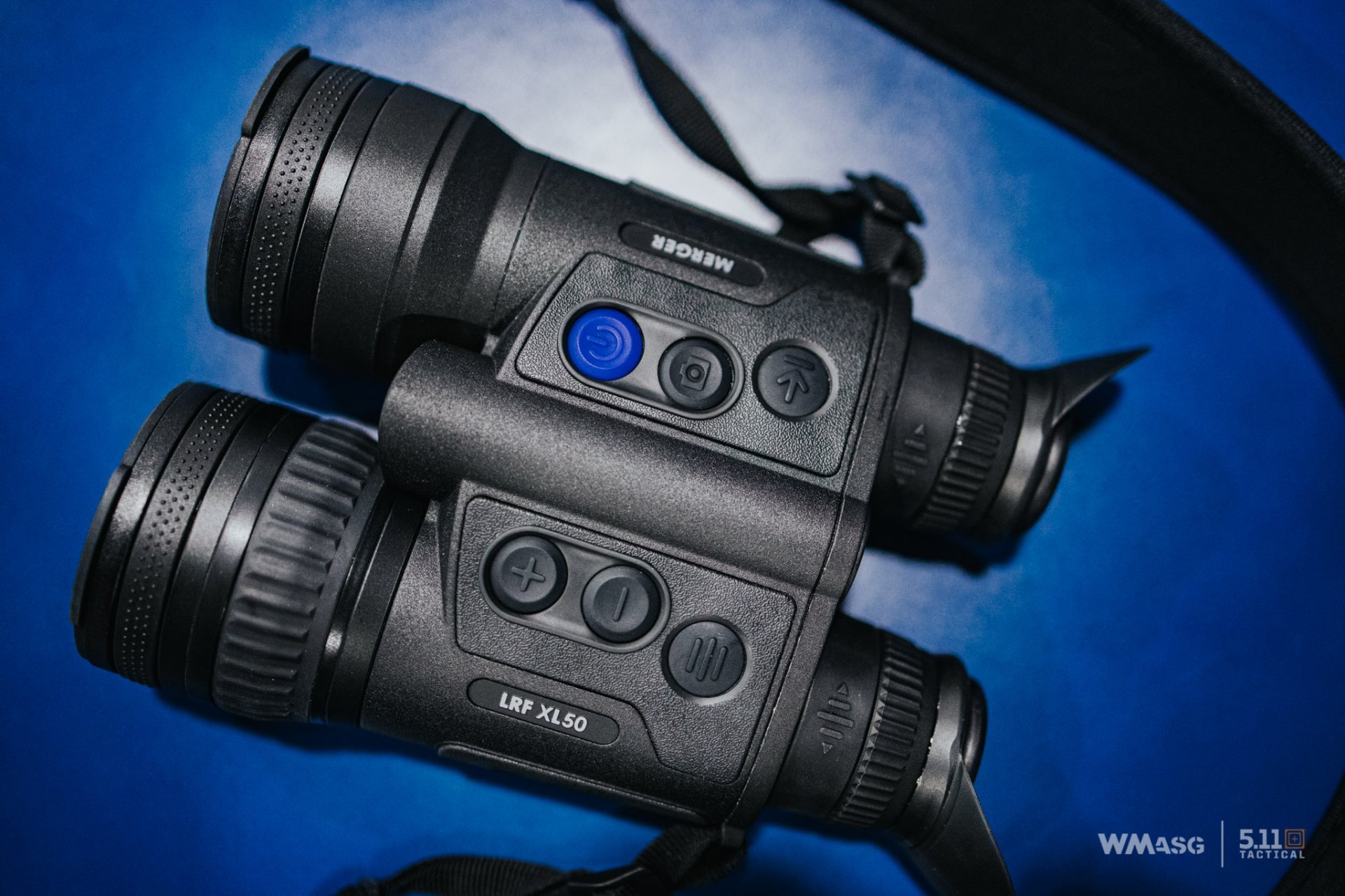
2023 Pulsar flagship thermal imaging binoculars - the Merger XL50 - allows to observe the environment in a native resolution of 1024x768 pixels.
Currently, in each type of thermal imaging devices, one of the following resolutions can be found most often: 160x120, 240x180, 256x192, 320x240, 384x288, 400x300, 640x480 and 640x512. In addition to the sporadic models with a matrix with a smaller number of pixels, there are also various types of imagers on the market with a resolution of 1024x768 or even 1280x1024, but models equipped with such sensors and intended for outdoor use began to appear on the market only in 2022. At the moment, their selection is limited and prices are high.
Thermal cameras with a matrix of 160x120 pixels are now treated as entry-level. In models without a large optical zoom, their real detection range of a human-sized object, under normal circumstances, often does not exceed several dozen meters. Under ideal conditions, it is possible to see the target at a slightly greater distance, but insufficient detail of the image is a significant impediment to its proper recognition. The increase in the practical range (at the expense of the field of view) may be affected by a larger base magnification of a given device. The problem is that few manufacturers decide to expand the cheapest product line and offer them in variants that differ in magnification.
2018. Leupold LTO Tracker Observation Thermal Imager external screen visible.
Slightly more possibilities are provided by devices with a resolution of 240x180 and 256x192 pixels. Here it is easier to have a wider selection of affordable models both in the form of handheld monoculars and simple thermal imaging sights, whose real detection range and image detail will be satisfactory for less demanding users. Models using 320x240 or 384x288 pixel matrices can be considered attractive solutions in terms of the price-performance ratio. Such thermal imagers are characterized by decent image quality, assuming that their thermal sensitivity and software are not a bottleneck. In addition, with the use of appropriate optics in favorable conditions allows to see objects distinguished by their temperature at distances counted in hundreds of meters.
2018. ATN Mars-HD sights are famous for a large number of implemented additional functions, however, using them may result in a delay in image display.
Those models that until recently were considered top shelf on the civilian market, i.e. thermal imagers with a matrix of 640x480 or 640x512 pixels, despite being dethroned by high-end resolutions of 1024x768 and 1280x1024, should still be considered as a quality solution. For example, a 640x480 resolution consists of about 3 times more pixels than popular medium priced devices. This translates into higher image detail, extended range and a more comfortable digital zoom experience.
2021 InfiRay Saim SCH50 thermal imaging sight. The device uses a 12 um 640x512 pixels sensor. It has a 50mm lens, f/1.1 aperture and base magnification of 2.9x.
Should the choice of the right image resolution be dictated only by the distances at which one plans to use the Imager? No - the more pixels the better. This feature is useful in every application, also when observing the target at a short distance. In addition to increasing the range of detection, recognition and identification, the high resolution also helps to aim more precisely and see both the observed target and elements in its surroundings, including those obscuring it, more clearly.
Basic magnification, field of view, lens size
Due to the limited capabilities of thermal sensors in the resolution category, imager manufacturers often try to provide the best possible image quality in other ways.
The method of improving image detail at a greater distance, which is eagerly used by manufacturers, is to increase the base optical zoom. It is worth considering that different values of this parameter will work better in sights, different in handheld monoculars or observation binoculars, and different still in a device that someone buys with the intention of wearing it on one's head. There are no universal truths here, even within the mentioned types of thermal imagers, the final choice depends on one's own preferences and the use of the equipment: hunting, mountain rescue, airsoft, etc. At the moment, there are no products that would offer smooth optical zoom transition, as is the case with classic types of observation and aiming optics. In the current decade, thermal imagers that allow a two-stage to switch between a smaller and a larger base magnification have appeared on the market. So one can expect that this feature will be developed over time.
2023 InfiRay Rico RH50 Pro is one of the first thermal imaging sights available on the civilian market that offers the possibility of two-stage change of the base zoom (while maintaining full, native resolution of the thermal sensor).
There are several factors that determine the actual base zoom of thermal imagers and one of them is the size of the lens. In many cases, achieving high values requires the use of large optics, which affects the price of the device, and often also its dimensions.
In return, many thermal imaging manufacturers offer a wide range of digital zoom options in their products. However, due to the low resolution of popular thermal sensors, the use of high digital zoom significantly affects the deterioration of image quality and increased pixelation. For this reason, the base optical magnifcation becomes an even more important selection criterion.
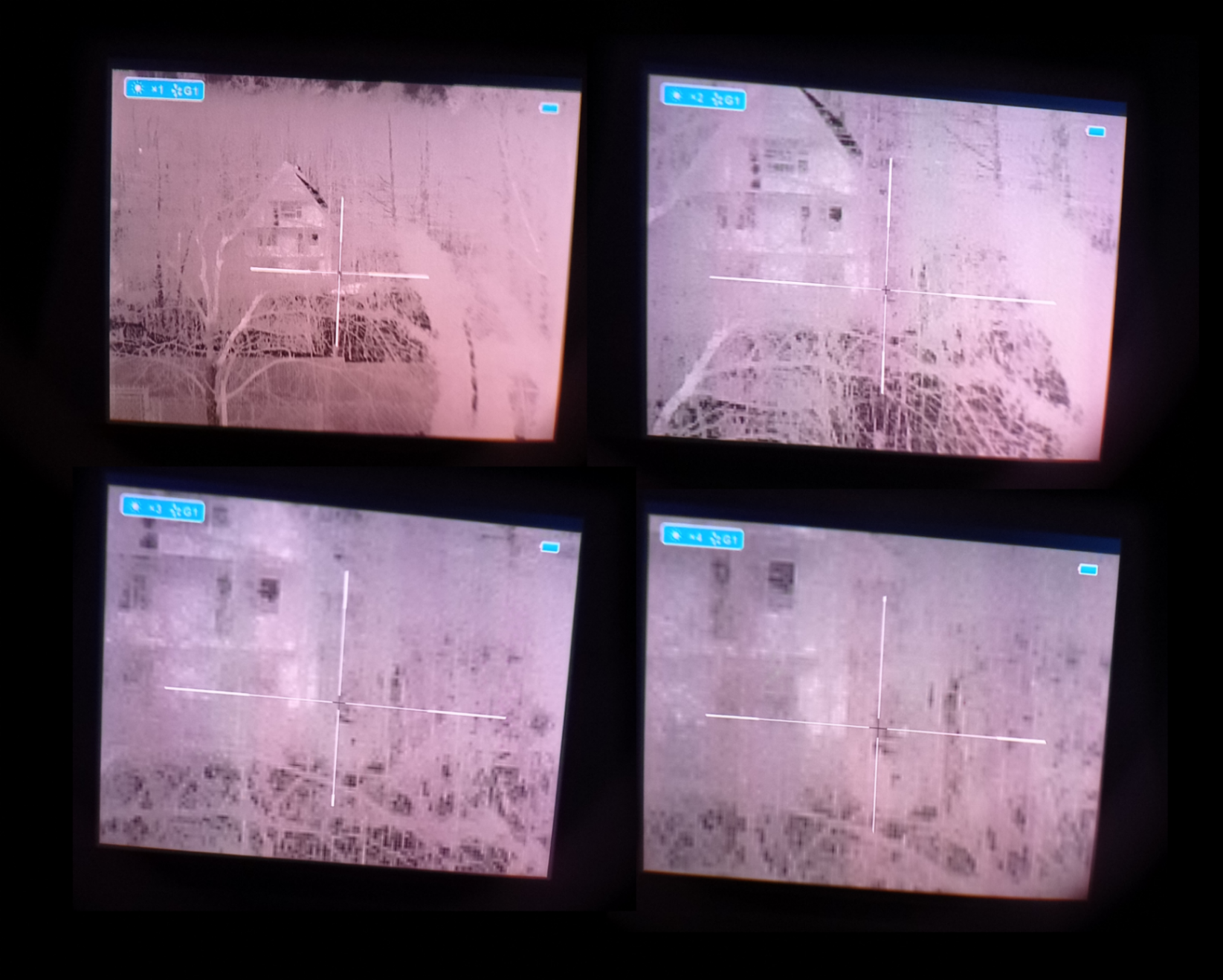
2023. Increasing the digital zoom level results in image pixelation.
A larger base zoom has a positive effect on the detail of the image at a longer distance, but most often it also narrows the field of view (similarly to classic optics). People considering the purchase of a sight, especially those who shoot at long distances, should be interested in thermal imagers with a high base zoom value, especially if the budget is limited to devices with a matrix with a lower resolution. However, it should be remembered that scanning the environment for a target with such a sight can be a nuisance. In such cases, the comfort of movement and observation can be supported by a second, handheld or head-worn Imager, with a lower base zoom and a larger field of view.
2020. Thermal imaging devices with lenses protected against solar reflections and the effects of hits during game using airsoft equipment. Pulsar Quantum XQ30V Lite, Delta Optical Neon S1, ATN Mars 4 384, Leupold LTO Tracker HD, and ATN Mars-HD 384 are shown.
The optimal choice may be different for people using thermal imaging at shorter distances: e.g. during activities with the use of airsoft equipment. Should one focus on comfortable and quick detection of threats or precise firing? The choice is not easy, and it can affect the effectiveness not only of the user himself, but also of his entire group.
Device range
When talking about the resolution of the sensor and the base magnification in relation to the range of the device, it is impossible to ignore this issue and briefly explain what "DRI" (Detection, Recognition, Identification) is.
In the technical specifications available on the websites of manufacturers and distributors, one can often find the declared range of the thermal imager. Sometimes only the maximum distance at which the device is able to detect the target (D) is given, and sometimes there is additional information about the possibility of its recognition (R) and identification (I).
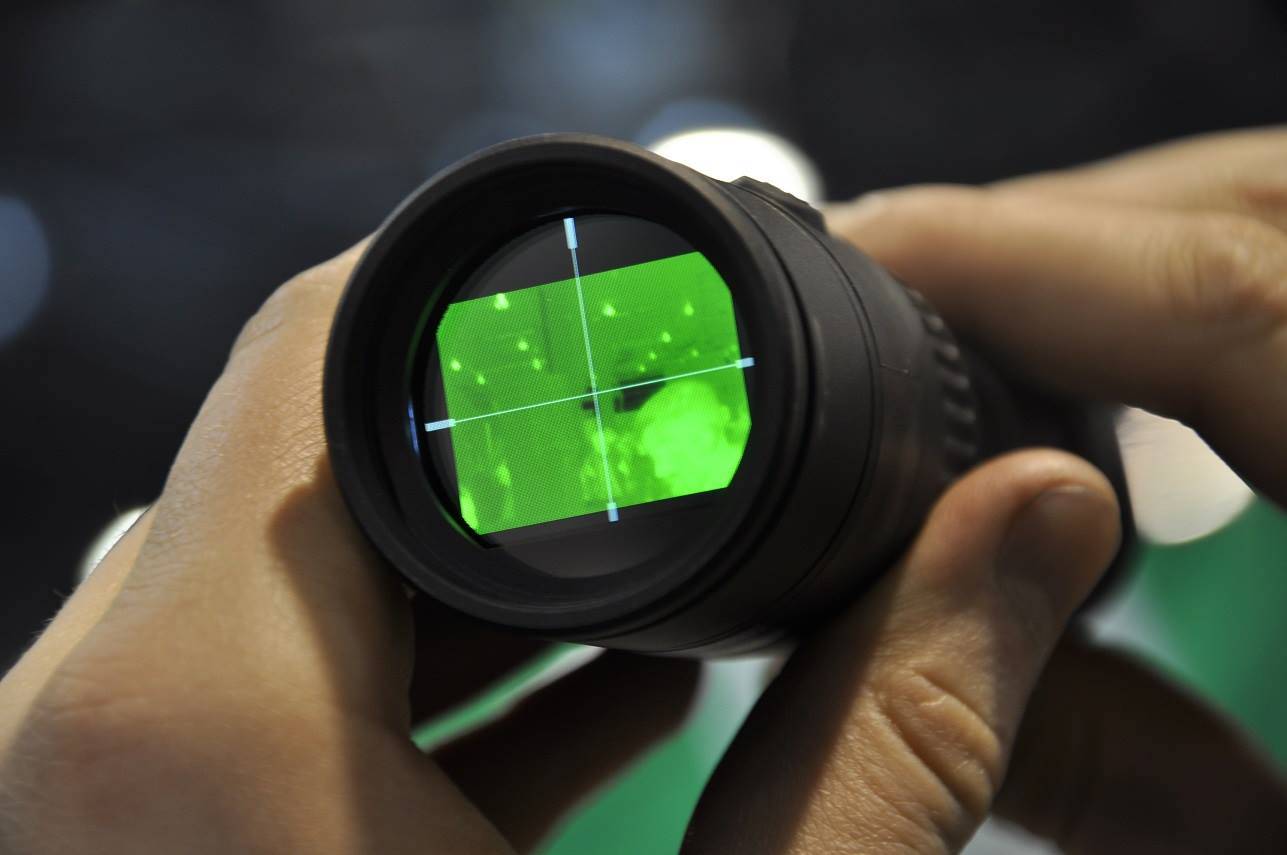
2020. Image visible in the older generation thermal imager - Pulsar Quantum XQ30V Lite in unfavorable weather conditions. The function to correct defective pixels is active.
The largest value is always for detection. This is a parameter that determines the maximum distance at which the device is able to detect a target (usually with dimensions similar to a human figure). Most often, however, this means that the object visible at the given distance, which is important, in ideal conditions, will be represented by only two pixels. So it's possible to say "there's something there", but nothing else.
The value presented as "recognition" may tell you a little more about the actual observation range. It mentions the distance from which it is possible to tell the class of an object, e.g. whether it is a human or a vehicle (minimum 6 pixels). If it is not mentioned in the description of the Imager, it can be assumed that the recognition range is about 3 times lower than the detection range.
The last parameter, identification, means the distance at which it is possible to distinguish further details (minimum 12 pixels). One can tell what type of vehicle one are watching, or whether the person one sees is a soldier or a civilian. The real range of identification is also about 3 times lower than recognition.
2022. Thermal imaging sights with a small base zoom also work well when used at close range. The photo shows the Hikmicro Thunder TH25 and Delta Optical Neon S1 models mounted on airsoft replicas intended for CQB games.
Taking all these factors into account, it is easier to determine at what distance the selected Imager will work in a practical application. If its detection range of a human-sized object is, for example, 1800 meters, then recognition should be possible from about 600 meters. Identification can take place only at a distance of 200 meters. Adding to this incomplete visibility of the silhouette or unfavorable weather conditions, one can expect an additional limitation of the actual range.
Refresh rate
There are thermal imagers on the market that differ in the refresh rate of the image. The most popular options are: 9 Hz, 25 Hz, 30 Hz, 50 Hz and 60 Hz.
2018. The old generation of FLIR PS24 Scout II Imagers offered a refresh rate of only 9 Hz. This does not provide sufficient comfort of use, working mainly when observing static scenes.
The higher the refresh rate, the more comfortable the imager is to use. It is worth knowing that for the observation of the terrain, with a fairly static scenery, a high refresh rate is not a necessary condition. However, in devices intended for aiming or moving around, image smoothness is very important. To maintain the proper comfort of using the thermal imager, it is worth considering especially models offering at least 30 Hz, and preferably more. However, this may result in increased power consumption.
Pixel size - 17 um or 12 um?
The technology used in thermal imaging devices currently on sale also differs in terms of pixel size. The most common are two values: 17 um and 12 um. How do they differ?
12 um allows the size of thermal sensors to be reduced. This, in turn, has an impact on, for example, lower cost of some components, such as optics. Smaller pixel size allows for greater magnification compared to 17 um technology, working with lenses of the same size. On the other hand, the 17 um pixel size can collect more data from the environment, which can translate into better image quality.
2020. Imager lenses are unfortunately prone to breaking. The cost of optics made of germanium can be much higher than that used in classic scopes, also high-end ones.
One has to remember, however, that the quality of sensors and software is constantly improving. Newer 12 um devices may provide as good (or better) image quality than older 17 um devices.
The second chapter of the part devoted to the technical parameters of thermal imaging devices will be published next Friday.
An earlier article on the basics, facts and myths, is available here.